Associated Apparatus
The associated apparatus is an energy-limiting device installed to protect the hazardous area apparatus from excess electrical energy being transmitted from the non-hazardous area signal source, or power supply.
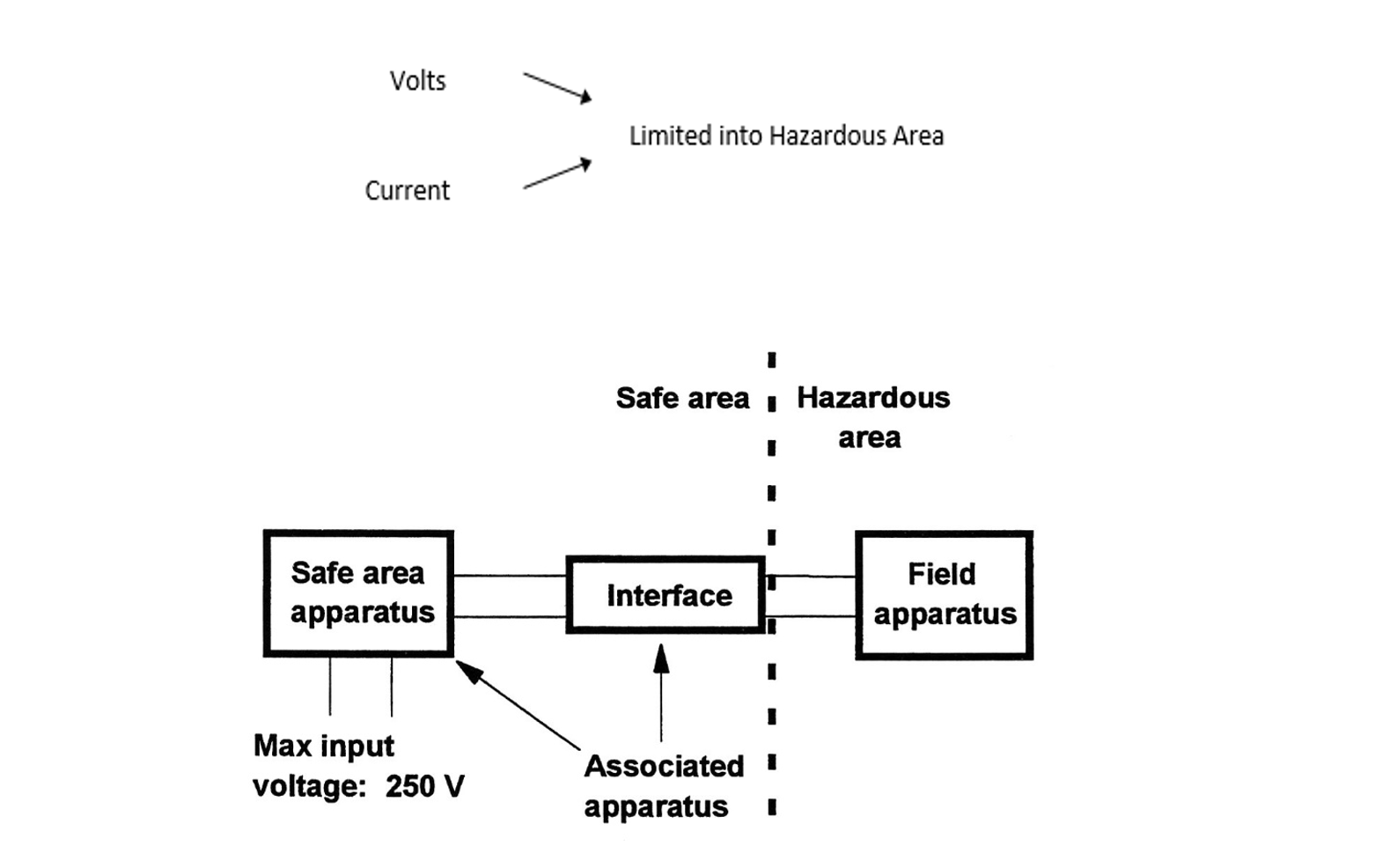
An energy limiting device, interface, is known as a barrier or isolator, depending upon the protection method chosen.
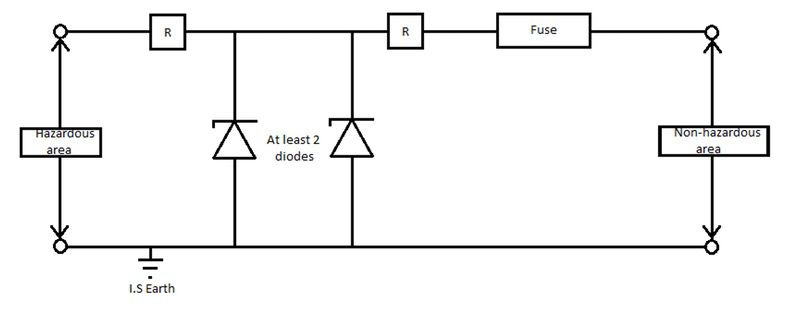
Barrier
A Barrier is a zener shunt diode circuit which uses the breakdown voltage property of the zener diode to limit under fault conditions the voltage that could be transmitted to the hazardous area apparatus.
Typical Zener Barrier
When the input voltage to the barrier is larger than the barrier rated voltage, typically 28 volt DC, the zener diode will begin to pass current. This fault current will blow the input fuse and isolate the hazardous area apparatus.
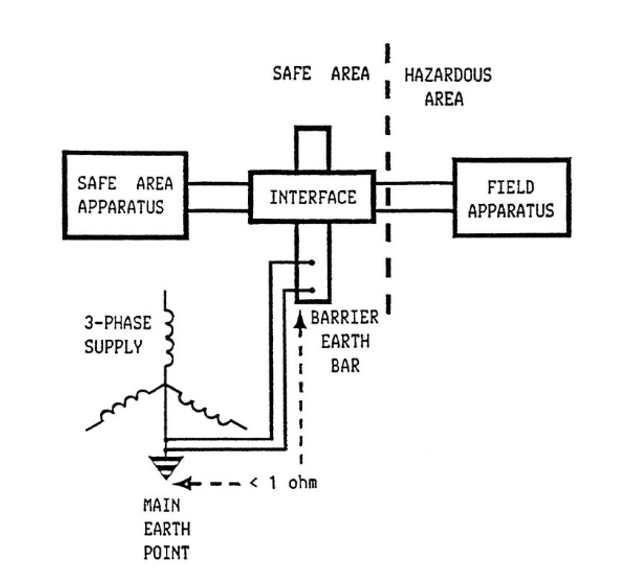
The zener barrier requires a good low resistance earth path to ensure sufficient fault current flows to blow the internal barrier fuse.
The earthing arrangement for shunt diode needs to be separated from the general earthing routes for motors and instrumentation.
The loop resistance of the earth conductor to earth point should be less than 1 ohm.
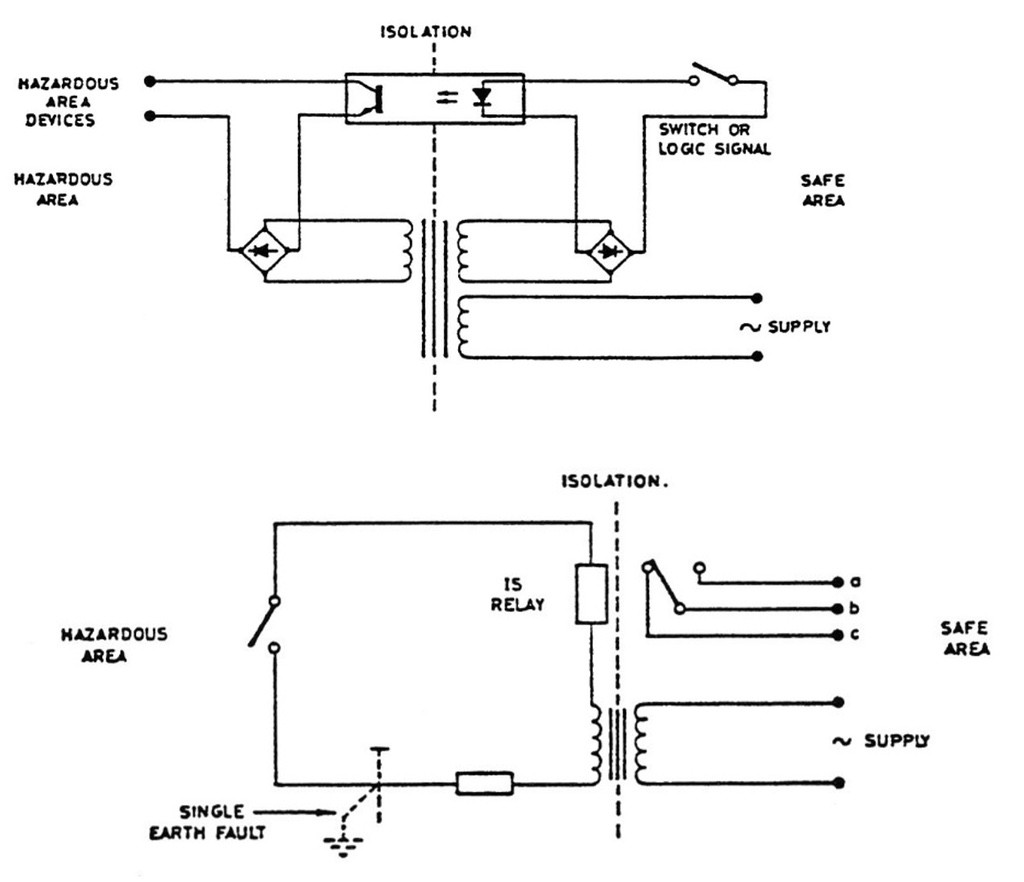
Isolator
Isolator associated apparatus is based on galvanic isolation (no electrical connection to another voltage source).
Methods of isolation used are transformer, relay contact, opto-isolator.